Diabetes is a disorder that causes a person's blood sugar level to become too high. There are three main types of diabetes: (1)
Type 1 diabetes: In type 1 diabetes, the body's immune system attacks and destroys the pancreas cells that produce insulin; usually, it occurs before the age of 25.
Type 2 diabetes: where the body dose does not produce enough insulin, or the body's cells do not react to insulin correctly, and as a result, blood sugar rises. Type 2 diabetes usually occurs due to obesity and overweight in people over 30 years of age. It more comment than type 1 diabetes, and about 80 to 90% of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes: Gestational diabetes happens when a pregnant women's blood glucose rises during pregnancy due to decreased body sensitivity to insulin. Of course, it does not happen in all pregnant women -Obese women are more likely to get the disease- and usually develops after birth.
Other types of diabetes are very uncommon, caused by certain diseases, infections, medications, etc.
If diabetes is left controlled, it will go many complications for the patient, like the above condition, and it can cause permanent damage to the patient and, finally, death. In 2016, an estimated 1.6 million deaths were directly caused by diabetes. Another 2.2 million deaths were attributable to high blood glucose in 2012. (10)
There is currently no means to prevent type 1 diabetes; however, it can prevent type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes. The best way to control type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes is to improve your lifestyle by eating a healthy and balanced diet.
In addition to a good diet for diabetes, regular physical activity and daily exercise can help you control your blood glucose levels.
If you are pre-diabetes or at risk of diabetes, do not worry. We are here to help you control your blood glucose and return to everyday life by adjusting your diet plan and lifestyle.

To prevent type 2 diabetes, you can follow these steps:
- Keep your weight in the healthy normal range and if you are overweight or obese, try to achieve a healthy weight with a good weight loss diet plan.
- Eat a healthy diet plan and consult a nutritionist to adjust your diet.
- Be active and exercise regularly, at least 30 minutes a day, 150 minutes a week.
- Avoid simple carbohydrates such as candy, sugar, sweeteners, white rice, etc.
- Reduce or avoid the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Avoid tobacco and smoking; these two increase the risk of diabetes and other chronic diseases.
Cause of the lack of insulin hormone production in type 1 diabetes, the primary treatment is insulin injection. Yet you can control your insulin intake and blood sugar levels by counting carbs.
Still, the primary treatment of type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes includes a proper diabetic diet plan and adequate physical activity to lower blood sugar levels and control other risk factors such as blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, etc.
The primary type of food that affects your blood sugar level is which one has carbohydrates. When you eat carbohydrates, it is broken down to glucose and absorbed into your blood, causing a rise in your blood sugar level.
Carbohydrate metabolism is essential in developing type 2 diabetes, which occurs when the body can't make enough insulin or can't properly use the insulin it makes. (11)
Therefore, you should prevent blood sugar spikes by counting the carbohydrates in your diabetic diet and dividing it into specific proportions throughout the day.
One of the most important things to look for in a diabetic diet is hypoglycemia, which is just as dangerous as hyperglycemia. Therefore, the diabetic diet should be adjusted to prevent hypoglycemia in diabetics. Hypoglycemia is especially true for those who exercise.
By monitoring the number of carbohydrates in a diabetic patient's diet, these complications can be prevented, and the disease's progression in the body can be prevented.
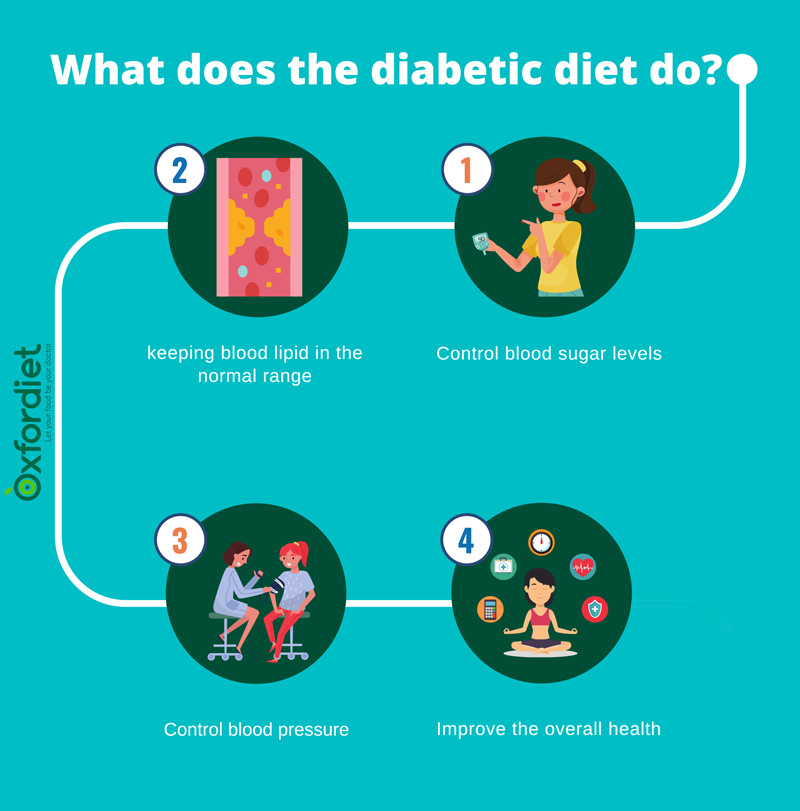
♦ Control blood sugar levels in the normal range with a good diabetic diet plan to prevent secondary complications of diabetes.
♦ Keeping normal levels of lipid profiles to prevent the prevention of cardiovascular disease
♦ Control blood pressure and reduce your blood pressure into the normal range
♦ Improve the overall health of the body by modifying your diabetic diet plan
The best way to manage diabetes is to change lifestyle with a diabetic diet plan and exercise. Following a healthy dietary plan for diabetic patients is a vital component of diabetes management because it can regulate blood glucose and lipid factors, resulting in weight reduction, improved response to pharmacotherapies, and optimal control of the patient's glycemic status and lipid profile. (12)
And exercise helps to weight management and controlling blood pressure and other cardiovascular risk factors.
For some patients, the best diet consists of the foods they are currently eating. But using a good diabetic diet for others is one of the most important steps. A diabetic patient's diet planning aims to balance the nutrients and control the body's blood glucose level with minimal cost. (13)
The first goal in a diabetic diet is to control blood sugar. In obese diabetics type 2, weight loss can also help lower blood sugar levels. (14) Therefore, a weight loss diet can also be helpful in these people.
A diabetic diet is a balanced diet with a moderate amount of food groups such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, etc. In the diabetic diet, sufficient fiber and sources of vitamins and minerals should be used to not suffer from a deficiency of these substances.
Another critical point in a diabetic diet is the regularity of meals. The diabetic diet should include at least three main meals and one snack in the late evening meal (In some cases, midmorning and midafternoon snacks are important to avoid hypoglycemia and an optimum diet plan consists 3 main meals and 3 snacks), and each of these meals should be eaten at specific times of the day. The number of carbohydrates in each of these meals should be adjusted according to each person's condition.
In the following, we want to talk about different macronutrients' importance in the diabetes diet:
To adjust your diabetic diet, you can refer to your nutritionist or get your online diet plan from us.
As we said, carbohydrates are the most crucial component of the diabetic diet.
Carbohydrates should make up a maximum of 45-50% of the energy intake of the diabetic diet. We suggest a low-carb or a Mediterranean diet for you, although research shows that a low-fat diet also helps control your blood sugar just like as a high-protein diet. (15)
In the diet plan of people with diabetes, the emphasis is on consuming various complex carbohydrates and whole grains and avoid simple carbs. The number of carbohydrates in the diet of a diabetic patient should be well settled and adjusted. The number of carbohydrates in each meal and snack should be consumed in a specific amount.
The amount of carbohydrates consumed in a diabetic diet is more important than the source of its use. Of course, it should be noted that in the diet plan of diabetics, the consumption of simple sugars such as sugar, industrial beverages, beverages, sweets, etc. should be limited and consumed complex carbs.
The nutritionist recommended using low glycemic index (GI) foods in the diabetic diet plan to control blood sugar.
Of course, you should know that in type 1 diabetes, we can control blood sugar by insulin injection, so there is no need to severe limit carbs. Still, it is important to timing, size, frequency, and composition of meals so as to avoid hypoglycemia or postprandial hyperglycemia.
Consumption of fiber and foods containing fiber in the diabetic diet plan is recommended. (15)
The recommended amount of fiber in a diabetic patient's diet is similar to healthy people and 20 to 35 grams per day (14g per 1000 calories). (16)
The beneficial effects of fiber on lowering lipid factors, preventing constipation and gastrointestinal disorders, and preventing gastrointestinal cancers have been proven. Still, the effect of increasing average dietary fiber intake on lowering blood sugar is not significant. However, it should be noted that consuming less than the recommended amount of fiber in the diet of people with diabetes can lead to secondary problems in these people.
Try to eat enough fiber-rich foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, etc. in your diet plan to prevent the secondary problem of diabetes Mellitus.
Protein plays a vital role in the health of the body and is essential for survival.
Since insulin disorder in people with diabetes affects glucose metabolism and does not directly affect amino acid metabolism, the body needs of people with diabetes are the same as normal people.
On the other hand, because protein sources are mostly free of carbohydrates - other than plant protein sources - they do not raise blood sugar, and you can eat them safely.
The diabetic diet's protein content is arranged in the same way as the diet of normal people. The minimum protein requirement for good diet plan is 0.9 g/kg/day (usual range, 1-1.5 g/kg/day), but a reduced protein intake is indicated in cases of nephropathy.
Fats should provide about 30% of the daily energy intake of the diabetic diet. In patients who do not have lipid disorder, 10% of dietary fats can be provided from saturated fats. The rest of the fats should be consumed unsaturated fats.
Patients who have serum lipid profiles disorder should reduce the amount of saturated fat in their diet plan to less than 7%.
Another thing to keep in mind about diabetic diet fats is the matter of food cholesterol; a low-cholesterol diet is recommended, which should be less than 300 mg per day.
Trans fatty acids in the diabetic diet plan, just like other people, can cause cardiovascular disease and gene mutations in the patient, so you should restrict fried foods, processed foods, chips, hydrogenated vegetable oils, etc. in your diet plan.
Reducing fat intake and maintaining it in the normal range in type 2 diabetic patient's diet over time will cause weight loss and improve the status of blood lipid factors.
People with diabetes who are not malnourished do not need to take vitamin and mineral supplements with their diabetes diet.
Supplements are recommended with the diet for diabetic people on extremely low-calorie diets, aged 65 years or older, vegetarians or vegans, pregnant or lactating women, patients who used medications that interfere with nutrient absorption, and patients in critical situations such as patients in ICU, etc.
In diabetic patients taking diuretics or uncontrolled blood glucose, magnesium supplementation is recommended. But before using a magnesium supplement, consult with your doctor. Chromium supplementation in patients with chromium deficiency can help improve their blood sugar levels.
Serum zinc levels in patients with diabetes decrease, and urinary excretion increases, so zinc deficiency in these patients is possible. Serum levels of zinc in people with diabetes should be in the normal range to insulin secretion continues. High or low levels of zinc in the body can affect insulin secretion in a diabetic patient.
Besides, normal levels of zinc in patients with diabetic foot ulcers help their wounds to heal faster. However, zinc's arbitrary consumption
can raise blood levels above average and have the opposite effect on insulin secretion. Therefore, before using any supplement, you need to talk with your doctor.
♦ Your diabetic diet should be regular, and you should care about timing.
♦ Avoid skipping or moving your diabetic diet plan meals without consulting your dietitian.
♦ Exercise lightly, such as walking for half an hour a day in the fresh air.
♦ Avoid anger, worry, and stressful situations.
♦ Carry a snack with 10 to 15 grams of carbohydrate to prevent hypoglycemia or treat it. For blood glucose of 51 to 70 mg/dL, treat with 10 to 15 g of fast-acting carbohydrate and 20-30 g of carbs for blood glucose ≤50 mg/dL.
♦ Minimize simple carbs such as sugar, chocolate, soft drinks, ice cream, sweet desserts, jellies, compotes, honey, jams, sweets, cakes, candies, etc.
♦ Dates, berries, raisins and dried fruits should also be reduced and consumed in the amount prescribed by your dietitian.
♦ In the diabetic diet, use traditional and whole-grain bread instead of white bread.
♦ Eat enough vegetables in your diet. It is better to eat fresh vegetables in the diabetic diet.
♦ Foods should be eaten boiled or steamed most time, and if you need to use oil in your diet, try to use olive and canola oils.
♦ Avoid using extra salt in your diet plan.
♦ At least twice a week, eat legumes in your diet for diabetics.
♦ Eat calmly and avoid eating when you are stressed or in a hurry.
♦ Avoid snacks and any food while watching TV.
♦ Use a diabetic diet adjusted by a certified dietitian.
Foods high in sodium: Food like sausages, baken or canned food, chips, puffs, processed foods, etc. have a lot of sodium.
Fatty foods with high cholesterol: Foods such as mayonnaise, high-fat meats, high-fat dairy, etc. should be limited in the diabetic diet.
Simple carbs: sweets, chocolates, biscuits, carbonated beverages, sugar, honey, jams, ice cream, etc. should be used in small amounts.
If you have had diabetes recently, you may wonder if eating fruits can be a problem for you or not?
The answer is NO, fruits are an excellent source of vitamins and minerals and should be involved in the diet of people with diabetes, but you should consider using them because of the glucose content of fruits.
Fruits are one of the principal sources of carbohydrates and should be used with caution in diabetic diets.
You can eat dried, fresh or frozen fruit, but it's important to how many use them.
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), you should count fruits as carbohydrates in the diabetic diet plan.
The best type of fruit for a diabetic diet is fresh fruits; fresh fruits contain fibre, water, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and other useful compounds. After that, no added sugar canned fruit or frozen fruit can be a good choice for a diabetic diet.
100% fruit juice is also dried fruit good choices for using a diabetic diet, but since fruit juice has no fibre and dried fruit lost its water, they may not be as filling as other choices. Besides, the sugar in these fruits is quickly absorbed and raises blood glucose levels.
Using fresh fruits slows type 2 diabetes progression, according to a study published in the (BMJ) British Medical Journal.
People with diabetes, when choosing fruits, should pay attention to its glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL).
The glycemic index is indicates how fast each food raises your blood sugar - glucose glycemic index = 100- . The lower the glycemic index cause slower rises in your blood sugar after eating.
Glycemic load is a more relevant factor for measuring the effect of food on blood sugar levels.
Low GI and low GL food are more suitable for use in a diabetic diet.
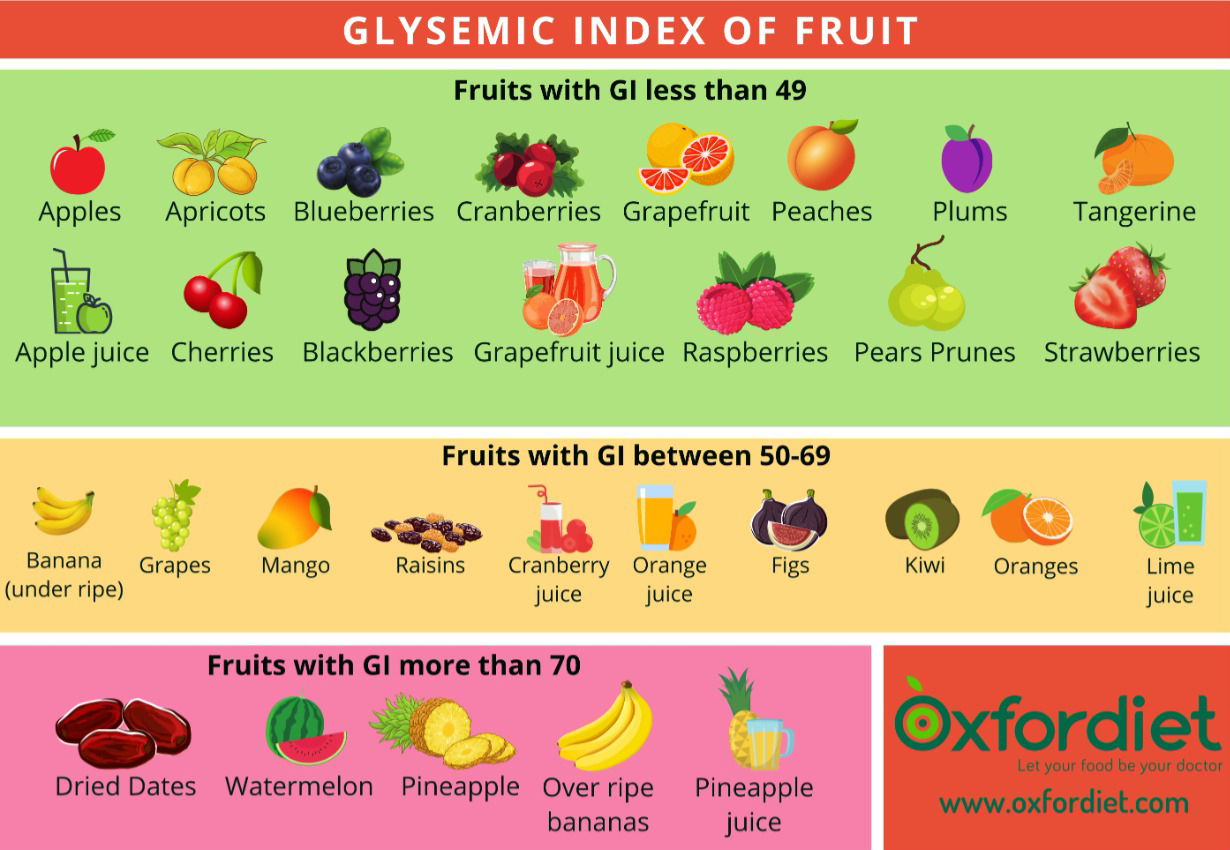
Below is a list of fruits that are categorized based on their glycemic index:
♦ Apples
♦ Apricots
♦ Blueberries
♦ Cranberries
♦ Grapefruit
♦ Peaches
♦ Plums
♦ Tangerine
♦ Apple juice
♦ Blackberries
♦ Cherries
♦ Grapefruit juice
♦ Pears Prunes
♦ Raspberries
♦ Strawberries
♦ Banana (under ripe)
♦ Grapes
♦ Mango
♦ Raisins
♦ Cranberry juice,
♦ Orange juice
♦ Figs
♦ Kiwi
♦ Oranges
♦ Orange juice
♦ Dried Dates
♦ Watermelon
♦ Over ripe bananas
♦ Pineapple
♦ pineapple juice
You should be the consideration of two points about the glycemic index of fruits:
First, the fruits' glycemic index may be slightly different from the above numbers depending on their growing conditions.
And second, fruits with a high glycemic index does not mean that you should not consume these fruits, but you should consume fewer of them.
The most guideline says that adult should eat at least five serving of fruits and vegetable per day. In diabetic people, this does not change. (17)
It is better to supply about 2 to 3 of these 5 serving to fruits. Note that this amount of fruit should be calculated in the carbohydrate count and subtract the number of fruit carbs from the total amount of carbohydrates allowed during the day.
Generally, vegetables are divided into two categories: starchy vegetables and non-starchy vegetables.
Due to the high carbohydrate content in starchy vegetables, they are classified as carbohydrates groups. So carbohydrate counting should be done on them and be used with caution in the diabetic diet.
Among starchy vegetables, we can mention potatoes, corn, beans, etc.
Non-starchy vegetables are among the healthiest foods that you can use in diabetic diets. Vegetables are rich in fibre, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are all essential for the body's health. By eating vegetables, in addition to controlling blood sugar, also helps to reach the essential needs of the body. Furthermore, due to the high fibre of vegetables, it helps increase the gastrointestinal tract's health and makes you feel fuller.
You have no restrictions on non-starchy vegetables, and you can use them in your diabetic diet as much as you want.
Non-starchy vegetable includes Asparagus, Brussels sprouts, Broccoli, Cabbage, Cauliflower, Celery, Cucumber, Eggplant, Mushrooms, Onions, Peppers, Salad greens, Spinach, Tomato, Zucchini, etc.
Warning! Vegetables should not be eaten in large amount in diabetic patients with kidney failure.
Another food group that people with diabetes should include in their diet is dairy.
Dairy products are essential in satisfying the body's need for calcium, potassium, Vitamine D, protein, and some other beneficial compound. Still, the most vital role of dairy is to provide the calcium needed by the body.
An important issue about dairy consumption in diabetics diet is the number of carbohydrates; each dairy serving has 12 grams of carbohydrates, which is equal to the number of carbohydrates in a serving of cereals. So the answer to this question is YES, it can raise your blood sugar.
Therefore if you want to use dairy in your diet, you need to calculate the number of carbs.
Do not forget to use 2 to 3 dairy servings a day to avoid osteoporosis and other middle-age problems. Consumption of dairy products is very important in children, teenagers and women.
Try low-fat dairy products, and be careful not to add sugar.