Inflammatory bowel disease, known as IBD, is a condition in which the digestive or gastrointestinal system suffers from inflammation. Therefore, an IBD diet and restriction in some substances are needed due to the disease's condition. There is no special and specific diet with the name of IBD diet, but we can use some restrictions and recommendations as IBD diet.
An inflammatory bowel disease is a group of diseases that the main types of them are called Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC). It is caused by the interaction between the immune system and the microbiota of the intestines. IBD diet is a helpful way to control and lower the suffering and painful symptoms besides medications.
* Crohn's disease: ongoing chronic inflammation of the bowel and affects the digestive tracts from mouth to anus.
Ulcerative colitis: Continuous inflammation from the rectum to the colon, spreading to all of the large intestines.
In these people, the disease's cause is unknown. Still, it may be a condition when genetic and environmental factors affect each other. Due to the interactions of genes and cells, the immune system attacks the intestine and its tissues' healthy inner cells and eventually brings inflammation there and complications in other parts of the body. IBD's biggest effect is on quality of life. The patients cannot do even their jobs properly because of IBD's troublesome effects on their lives.
♦ Abdominal pain, swelling, cramps
♦ Bloody diarrhea
♦ Weight loss
♦ Fatigue
♦ Fever
♦ Pain in joints
♦ Anemia
♦ Undesired weight loss
♦ Intestinal ulcers and bleeding at those sites
♦ Hole and perforations in the guts
♦ The narrowness of the intestine mostly in Crohn's
♦ Toxic megacolon
♦ Fistulae, perianal disease
♦ Malnutrition and deficiencies
There is no specific way to prevent IBD occurrence due to the genetic part of this disease. Still, it can be controlled like chronic diseases through diet.
We don't have any exact IBD diet. Still, there are many recommendations and self-cares to modify and monitor the symptoms and relieve the painful symptoms.
There are a lot of medications, but this disease can't be cured entirely and go away. Stem cell therapy is a novel and modern way to help IBD patients. Still, the IBD diet and meal planning for IBD, which dietitians suggested and designed, is the best way to control the disease.
There are several diets to control the symptoms of IBD, one of which is used according to each person's condition. include:
♦ SCD diet
♦ AID diet
♦ Gluten-free diet
♦ Low-carb diet
♦ Low fibre diet
♦ Low FODMAP diet
♦ Low residue diet
♦ Liquid nutrition diet
♦ Mediterranean diet
♦ Exclusive enteral nutrition
For a dietitian against an IBD disease, the first approach is to reduce fibre and dairy intake. But some soluble dietary fibres help the intestines to reduce the lesions of mucosa. Putting SCFAs (short-chain fatty acids), which are available in cheese and butter, can have an immune regulation effect. They speed up the functions of healing and repair of inner intestinal tissues.
It is suggested to consume small and repeated meals.
There has been a diet used for the health of the intestine called SCD or Specific Carbohydrate Diet from the 1920s. This Carbohydrate exclusion diet has been used for a lot of research to determine the treatments for colitis and Crohn's diseases. This diet is based on eliminating some of the carbs which are hard to digest. Most vegetable fruits, organic meats, and fish are allowed, but many processed foods, sugar, starches, and grains are not allowed.
A low residue diet can help IBD patients to have a reduction in their symptoms. This diet has less amount of fibres and residues, which reduces the number of daily bowel movements. The amount of stool will be decreased subsequently. This restricted diet helps to omit the intestines' undigested foods, and it is the best diet for tolerating the symptoms of pains.
Liquid nutrition in a diet named exclusive enteral nutrition has been used for children with Crohn's disease. This diet consists of soups, shakes, and juices that make the digestion process more comfortable and easier than eating any solid diet. Going on a liquid diet does not require the gut's hard movements, and the foods will pass through the intestines comfortably.
AID (Anti Inflammatory diet) is based on the SCD diet. Prebiotics, probiotics, the foods to avoid, and the foods IBD patients should eat, and how to eat them during their diet are supposed to be observed in the AID-IBD diet.
Probiotics: The live microorganisms existing in gut flora such as safe and healthy bacteria and yeast which help the immune system, prevent constipation, relieving the gut or intestinal pain, etc.
Such as Plain yogurt, fermented veggies, kefir, miso, aged cheese
Prebiotics: The compounds and food substances used and consumed by probiotic microorganisms, including fibres that are indigestible and are not absorbed by the body, so it can be a portion of food to feed the gut microbiome.
Such as groat, bananas, chia, flaxseed, hemp seed, garlic, onion, chicory root, leeks, artichokes, asparagus
This AID-IBD diet is divided into three phases. Each phase is taking measures due to the condition and percentage of the problem the sufferer is experiencing.
Phase 1: the foods in this diet phase help the IBD patients have immediate and urgent works to relieve pains. This phase is useful for recently hospitalized patients. The diet is blended and soft with a smooth texture that is easily tolerated.
Phase 2: the severe symptoms have been healed a little, and more recommendations are needed to have fewer symptoms. In this phase, the fibre can be tolerated, but the IBD patients still have painful movements and indigestion problems. More soluble fibre and vegetables can be used in the IBD diet.
Phase 3: in this phase, patients can eat more foods in different types such as stir foods, meats, whole beans, etc.
Exclusive enteral nutrition therapy (EEN) in pediatric Crohn's disease can be done. Still, there is less evidence in taking the measure of this therapy for ulcerative colitis patients. Mineral deficiencies such as Zinc, Magnesium, Selenium are common, so supplements are needed.
Enteral nutrition has been efficient in improving hemoglobin levels in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, especially combined with erythropoietin.
There are many foods that you can eat on IBD diet, include:
♦ Dairy products milk yogurt, cheese, creamy soups
♦ Ripe fruits Bananas Apricots, melon, plums, cantaloupe, peaches, watermelon, juices without pulps, applesauce
♦ Cooked veggies perfectly cooked pumpkin, squash, eggplant, spinach, potatoes, beans, asparagus, beets, carrots without skins or seeds
♦ Refined grains low white fibre bread, white rice, dry cereals, corn flakes
♦ Proteins eggs, fish, cooked, meat, no skin poultry, bacon, smooth peanut butter, smooth sesame butter, or tahini without seeds
♦ Tomatoes, peppers, tomatillos or Mexican husk tomato, berries, honey,
Some foods are categorized as the triggers of the bowel's inflammatory, but they also differ from person to person. For example, some food may irritate a person's bowel with IBD, but it may be ok and with no symptoms to another IBD patient.
Raw fruits, soy, sugar, lactose, gluten, leafy vegetables, peppers, chilli peppers, spicy foods, popcorn, corn, legumes, bran cereals, Okra, alcohol, caffeine, fatty foods and processed foods you should care about them and eat them with caution.
You have to limit the fat intake to under five g/serving and use plant oils more.
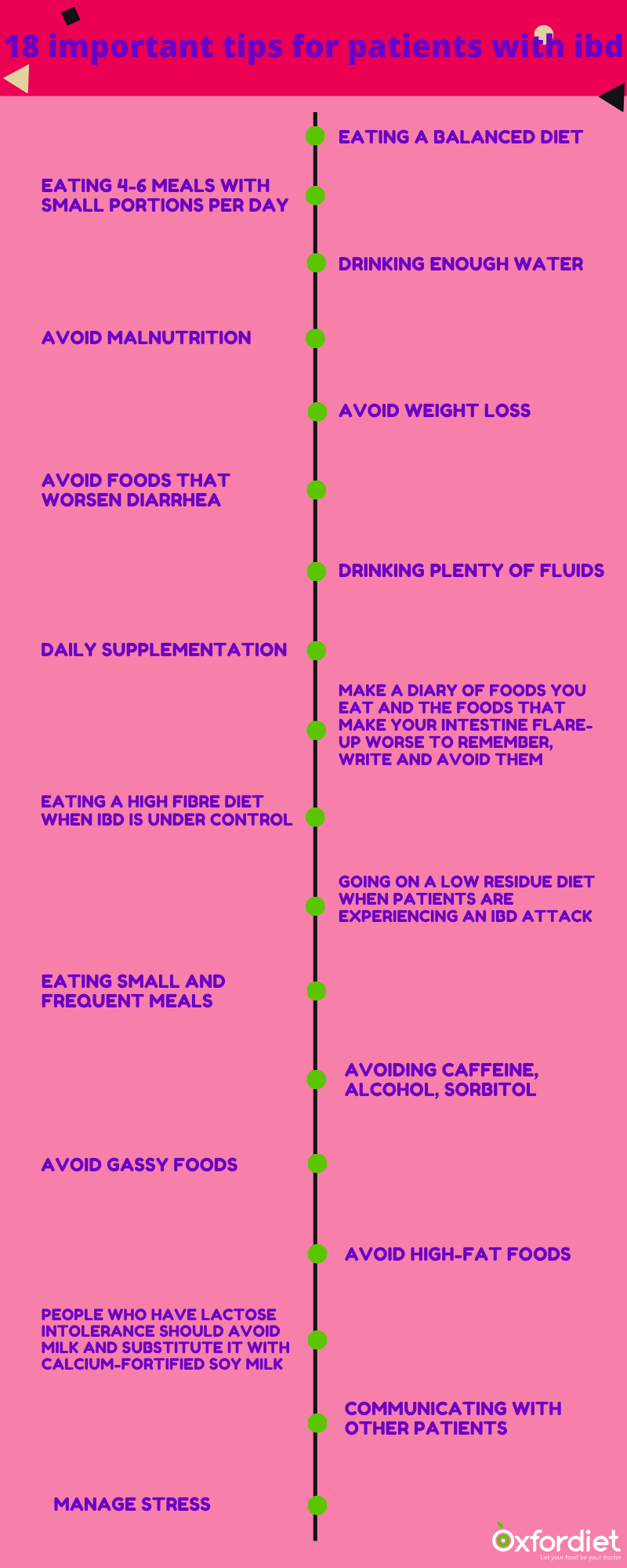
♦ Eating a balanced diet in macronutrients and essential micronutrients and adequate in energy
♦ Eating 4-6 meals with small portions per day
♦ Drinking enough water and staying hydrated
♦ Avoid malnutrition
♦ Avoid weight loss
♦ Avoid foods that worsen diarrhea
♦ People who have lactose intolerance should avoid milk and substitute it with calcium-fortified soy milk
♦ Drinking plenty of fluids
♦ Daily supplementation of multivitamin and minerals (before using any kind of supplement consult with a dietitian)
♦ Make a diary of foods you eat and the foods that make your intestine flare-up worse to remember, write and avoid them
♦ Eating a high fibre diet when IBD is under control
♦ Going on a low residue diet when patients are experiencing an IBD attack
♦ Eating small and frequent meals
♦ Avoiding Caffeine, alcohol, sorbitol
♦ Avoid gassy foods
♦ High-fat foods can cause diarrhea, so they should be avoided
♦ Communicating with other patients
♦ Manage stress
Supplementation may be needed in a restricted diet. To maintain the vitamins and minerals that have been omitted through the IBD diet should be added in supplement form. So you can talk to your doctor or registered dietitian about them.
Psyllium supplement that is a mixture of soluble and insoluble fibres can relieve the symptoms of IBD besides IBD diet, reduce the inflammation, and help the mucosal tissue of inner intestinal.
Parenteral iron supplementation can be used due to the anemia occurring after bleeding in gut tracts.
Vitamin B
Fat-soluble vitamins (Vitamin D and Vitamin E)
Essential fatty acids
Calcium